Servo Motor and Controller Guide
Learn about servo motors and servo motor controllers in this guide, including: how servo motors work, how to choose a servo motor, types of servo motors, and more.
Replaced by the 3212_0 - SpringRC High Torque Servo Continuous Rotation (SM-S4315R).
The 3210 is a small-sized servo that has been built by SpringRC specifically for continuous rotation (up to 80 RPM at 4.8 V), and it produces a fair amount of torque (2.1 kg-cm at 4.8 V). It features two ball bearings on the output shaft for reduced friction, and it offers easy access to the rest-point adjustment potentiometer. Essentially, it is a gear motor that can be controlled by an RC servo controller. It is not normally used as an actuator, as there is no way of commanding it to move to a particular position, as a standard RC servo does.
The 3210 continuous rotation servo converts RC servo position pulses into continuous rotation speed. The default rest point is 1.5 ms, but this can be adjusted by using a small slotted screwdriver to turn the middle-point positioner (see the Mechanical Drawing). Pulse widths above the rest point result in counterclockwise rotation, with speed increasing as the pulse width increases; pulse widths below the rest point result in clockwise rotation, with speed increasing as the pulse width decreases.
Normal servos can be adapted to continuous rotation use, but the problem is that the range of positions that result in the motor being stopped or operating at less than maximum speed is very narrow. Continuous rotation servos, depending on the position commanded, can go forward or reverse at different speeds. With an adapted continuous rotation servo, the position range for the different speeds is very narrow, making it difficult to produce a specific speed.
These dedicated continuous rotation servos are superior because they have a very wide “deadband” so you can be sure the motor is stopped when you command it, and the position range for forward or reverse motion is very wide, giving lots of speed resolution.

| Motor Properties | |
|---|---|
| Motor Type | Continuous Rotation Servo |
| Rated Torque | 2.1 kg·cm |
| Rated Speed | 80 RPM |
| Physical Properties | |
| Gear Train Material | Metal |
| Bearing Type | Double Ball Bearing |
| Motor Length | 28.6 mm |
| Motor Width | 31.3 mm |
| Motor Depth | 16.5 mm |
| Wire Length | 180 mm |
| Weight | 19 g |
| Electrical Properties | |
| Rated Voltage | 4.8 V DC |
| Rated Current (on 1061 controller) | 75 mA |
| Rated Current (on 1066 controller) | 80 mA |
| Stall Current (on 1061 controller) | 700 mA |
| Stall Current (on 1066 controller) | 415 mA |
| Customs Information | |
| Canadian HS Export Code | 8501.10.00 |
| American HTS Import Code | 8501.10.40.60 |
| Country of Origin | CN (China) |
This Servo can be used with the following Phidget motor controllers:
The 1061 will produce a little more torque than the 1066.
When connecting the servo motor to the motor controller, make sure that the cable wires line up with the proper colors as marked on the conroller board.
The motor is stopped at Target Position 50 (the stopped position is actually a range that goes from 45 to 55 depending on your motor). When you change the target motor position to a value less than your motor’s “stop range,” the motor will rotate counter-clockwise. When you change the target motor position to a value higher than your motor’s “stop range,” the motor will rotate clockwise.
Speed is controlled by changing the motor target position. As you move further away from the “stop position,” the motor will increase speed until it reaches maximum speed. Acceleration can be controlled by using the velocity property in the PhidgetAdvancedServo.

|
RC servos are hobbyist remote control servos typically used in radio-controlled models, where they provide actuation for various mechanical systems such as the steering of a car, the flaps on a plane, or the rudder of a boat. These servos are not industrial grade and are not recommended for continuous heavy use. |
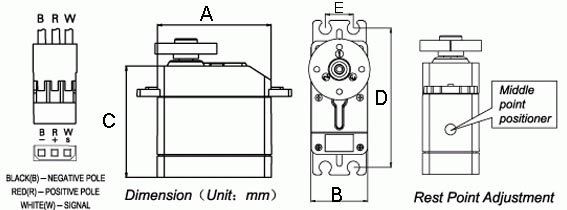
| A | B | C | D | E |
| 31.3mm | 16.5mm | 28.6mm | 38.1 | 8.1mm |