Template:VINTTable: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
[[Image:vint-v.jpg|350px|link=]] | [[Image:vint-v.jpg|350px|link=]] | ||
This mode is for connecting to a VINT device. | This mode is for connecting to a VINT device. The VINT Hub and VINT device communicate using a digital protocol. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
[[Image:vint-di.jpg|280px|link=]] | [[Image:vint-di.jpg|280px|link=]] | ||
In digital input mode, the VINT Hub port can act as an active-low digital input. This mode is great for reading the state of buttons and | In digital input mode, the VINT Hub port can act as an active-low digital input. This mode is great for reading the state of buttons, switches, and any other logic-level input. | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
[[Image:vint-vr.jpg|280px|link=]] | [[Image:vint-vr.jpg|280px|link=]] | ||
In voltage ratio input mode, the VINT Hub port will read the voltage on the white wire and compare it to the voltage | In voltage ratio input mode, the VINT Hub port will read the voltage on the white wire and compare it to the voltage supplied on the red wire. This mode will let you read any ratiometric Phidget sensor. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
[[Image:vint-vi.jpg|280px|link=]] | [[Image:vint-vi.jpg|280px|link=]] | ||
In voltage input mode, the VINT Hub port will read the voltage on the white wire. This can be used to interface a non-ratiometric sensor | In voltage input mode, the VINT Hub port will read the voltage on the white wire. This can be used to interface a non-ratiometric sensor or to measure the voltage in a 5V digital circuit. | ||
| | | | ||
=== Digital Output Mode === | === Digital Output Mode === | ||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
[[Image:vint-do.jpg|280px|link=]] | [[Image:vint-do.jpg|280px|link=]] | ||
In digital output mode, a VINT Hub port can behave like a 3.3V digital output. You could use this mode to blink an LED or switch on a MOSFET | In digital output mode, a VINT Hub port can behave like a 3.3V digital output. You could use this mode to blink an LED or switch on a MOSFET. | ||
|} | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 18:01, 1 September 2023
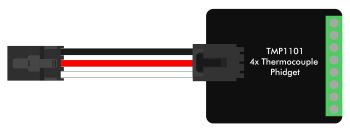
VINT Device Mode
This mode is for connecting to a VINT device. The VINT Hub and VINT device communicate using a digital protocol. | |
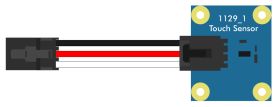
Digital Input Mode
In digital input mode, the VINT Hub port can act as an active-low digital input. This mode is great for reading the state of buttons, switches, and any other logic-level input. |
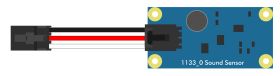
Voltage Ratio Input Mode
In voltage ratio input mode, the VINT Hub port will read the voltage on the white wire and compare it to the voltage supplied on the red wire. This mode will let you read any ratiometric Phidget sensor. |
Voltage Input Mode
In voltage input mode, the VINT Hub port will read the voltage on the white wire. This can be used to interface a non-ratiometric sensor or to measure the voltage in a 5V digital circuit. |
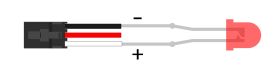
Digital Output Mode
In digital output mode, a VINT Hub port can behave like a 3.3V digital output. You could use this mode to blink an LED or switch on a MOSFET. |