Parts
Before getting started, make sure you have the following parts.
Setup
Step 1
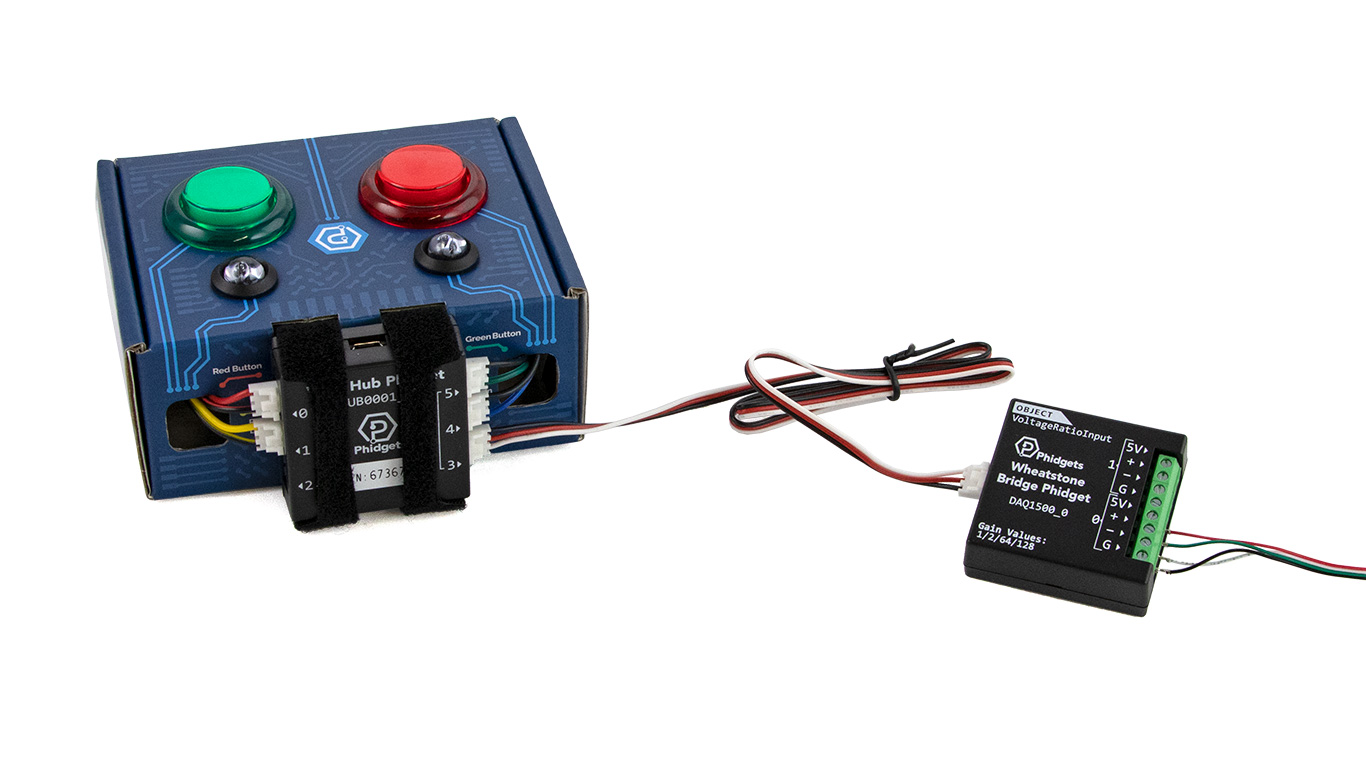
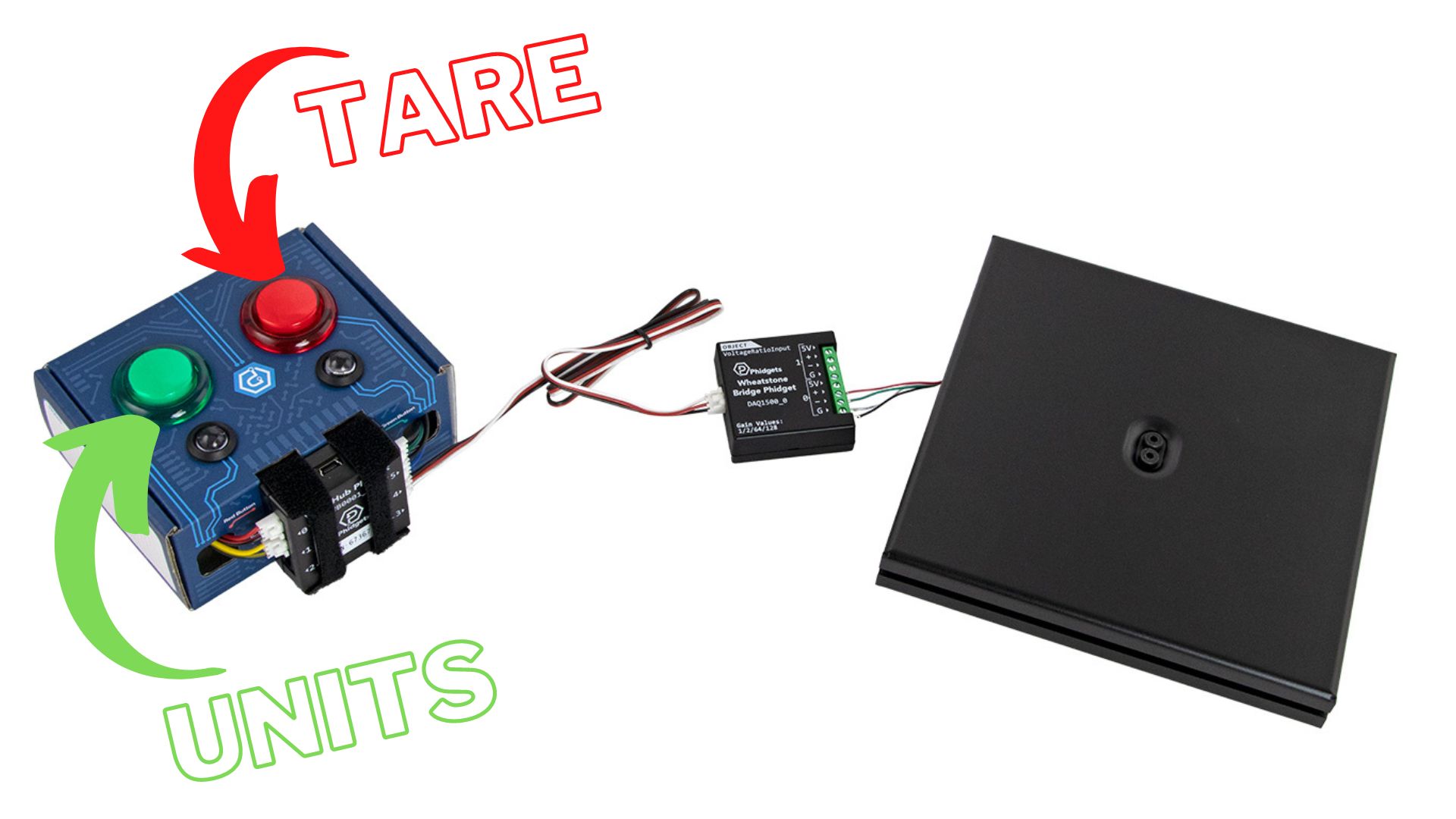
Connect your Wheatstone Bridge Phidget to Hub Port 3 as shown in the images.
If you haven't used your Getting Started Kit yet, first complete the Getting Started Kit tutorial.
Taring Scale
In this section, you will create a taring functionality for your scale by using the red button.
Taring a scale will reset the output to 0. This is useful for a variety of reasons. For example, if you were measuring the weight of a liquid, you could place a container on your scale, tare the scale (reset output to 0), and then simply measure the amount of liquid you need.
Write code (Java)
Copy the code below into a new Java project. If you need a reminder of how to do this, revisit the Getting Started Course.
Not your programming language? Set your preferences so we can display relevant code examples
import com.phidget22.*;
public class TareUnits {
//Define
static VoltageRatioInput scale;
static DigitalInput tareButton;
public static double tareScale()throws Exception{
double average = 0;
int count = 0;
//Set data interval to minimum so we can get data faster
scale.setDataInterval(scale.getMinDataInterval());
System.out.println("Taring Scale...");
while(count < 32){
average += scale.getVoltageRatio();
count += 1;
Thread.sleep(20);
}
//Reset data interval
scale.setDataInterval(250);
return average/count;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//Create
scale = new VoltageRatioInput();
tareButton = new DigitalInput();
//Address
tareButton.setHubPort(0);
tareButton.setIsHubPortDevice(true);
//Open
scale.open(1000);
tareButton.open(1000);
//Offset value
double offsetValue = 0.0;
//Automatically tare scale
offsetValue = tareScale();
//Use your Phidgets
while(true){
//Calculate Weight (kg)
double weight = 4700 * (scale.getVoltageRatio() - offsetValue);
//Display Weight
System.out.println(String.format("%.3f kg", weight));
if(tareButton.getState()){
offsetValue = tareScale();
}
Thread.sleep(250);
}
}
}
package tareunits;
import com.phidget22.*;
public class TareUnits {
//Define
static VoltageRatioInput scale;
static DigitalInput tareButton;
public static double tareScale()throws Exception{
double average = 0;
int count = 0;
//Set data interval to minimum so we can get data faster
scale.setDataInterval(scale.getMinDataInterval());
System.out.println("Taring Scale...");
while(count < 32){
average += scale.getVoltageRatio();
count += 1;
Thread.sleep(20);
}
//Reset data interval
scale.setDataInterval(250);
return average/count;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//Create
scale = new VoltageRatioInput();
tareButton = new DigitalInput();
//Address
tareButton.setHubPort(0);
tareButton.setIsHubPortDevice(true);
//Open
scale.open(1000);
tareButton.open(1000);
//Offset value
double offsetValue = 0.0;
//Automatically tare scale
offsetValue = tareScale();
//Use your Phidgets
while(true){
//Calculate Weight (kg)
double weight = 4700 * (scale.getVoltageRatio() - offsetValue);
//Display Weight
System.out.println(String.format("%.3f kg", weight));
if(tareButton.getState()){
offsetValue = tareScale();
}
Thread.sleep(250);
}
}
}
//Add Phidgets Library
import com.phidget22.*;
//Define
VoltageRatioInput scale;
DigitalInput tareButton;
double offsetValue = 0.0;
double tareScale() throws Exception{
double average = 0;
int count = 0;
//Set data interval to minimum so we can get data faster
scale.setDataInterval(scale.getMinDataInterval());
println("Taring Scale");
while(count < 32){
average += scale.getVoltageRatio();
count += 1;
delay(20);
}
//Reset data interval
scale.setDataInterval(250);
return average/count;
}
void setup(){
try{
//Create
scale = new VoltageRatioInput();
tareButton = new DigitalInput();
//Address
tareButton.setHubPort(0);
tareButton.setIsHubPortDevice(true);
//Open
scale.open(1000);
tareButton.open(1000);
//Automatically tare scale
offsetValue = tareScale();
}catch(Exception e){
//Handle Exceptions
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
void draw(){
try{
//Use your Phidgets
//Calculate Weight (kg)
double weight = 4700 * (scale.getVoltageRatio() - offsetValue);
//Display Weight
println(String.format("%.3f kg", weight));
//Tare Scale
if(tareButton.getState()){
offsetValue = tareScale();
}
delay(250);
}catch(Exception e){
//Handle Exceptions
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
Write Code (Python)
Copy the code below into a new Python project. If you need a reminder of how to do this, revisit the Getting Started Course.
Not your programming language? Set your preferences so we can display relevant code examples
#Add Phidgets Library
from Phidget22.Phidget import *
from Phidget22.Devices.VoltageRatioInput import *
from Phidget22.Devices.DigitalInput import *
#Required for sleep statement
import time
def tareScale():
average = 0
count = 0
print("Taring Scale...\n")
#Set data interval to minimum so we can get data faster
scale.setDataInterval(scale.getMinDataInterval())
while(count < 32):
average += scale.getVoltageRatio()
count += 1
time.sleep(0.02)
#Reset data interval
scale.setDataInterval(250)
return average/count
#Create
scale = VoltageRatioInput()
tareButton = DigitalInput()
#Address
tareButton.setHubPort(0)
tareButton.setIsHubPortDevice(True)
#Open
scale.openWaitForAttachment(1000)
tareButton.openWaitForAttachment(1000)
#Use your Offset Value
offsetValue = 0
#automatically tare scale
offsetValue = tareScale()
#Use your Phidgets
while(True):
#Calculate Weight (kg)
weight = 4700 * (scale.getVoltageRatio() - offsetValue)
#Display Weight
print("%.3f kg" % weight)
#tare scale
if(tareButton.getState()):
offsetValue = tareScale()
time.sleep(0.25)
Write code (C#)
Copy the code below into a new C# project. If you need a reminder of how to do this, revisit the Getting Started Course.
Not your programming language? Set your preferences so we can display relevant code examples
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Phidget22;
namespace TareUnits
{
internal class Program
{
//Define
static VoltageRatioInput scale;
static DigitalInput tareButton;
static double tareScale()
{
double average = 0;
int count = 0;
//Set data interval to minimum so we can get data faster
scale.DataInterval = scale.MinDataInterval;
System.Console.WriteLine("Taring Scale ...");
while (count < 32)
{
average += scale.VoltageRatio;
count += 1;
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(20);
}
//Reset data interval
scale.DataInterval = 250;
return average / count;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create
scale = new VoltageRatioInput();
tareButton = new DigitalInput();
//Address
tareButton.HubPort = 0;
tareButton.IsHubPortDevice = true;
//Open
scale.Open(1000);
tareButton.Open(1000);
//Scale offset
double offsetValue = 0.0;
//Automatically tare scale
offsetValue = tareScale();
//Use your Phidgets
while (true)
{
//Calculate Weight (kg)
double weight = 4700 * (scale.VoltageRatio - offsetValue);
//Display Weight
System.Console.WriteLine(weight.ToString("F3") + " kg");
if (tareButton.State)
{
offsetValue = tareScale();
}
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(250);
}
}
}
}
Write code (Swift)
Copy the code below into a new Swift project. If you need a reminder of how to do this, revisit the Getting Started Course.
Not your programming language? Set your preferences so we can display relevant code examples
Code not available.
Run Your Program
Try running your program. Your scale will automatically tare itself to begin, and then every time you press the red button, it will re-tare itself.
Changing Units
In this step, you will modify your code from the previous step and add unit-changing functionality. When a user presses the green button, your program should cycle between the following units:
- grams (starting unit)
- ounces
- A unit of your choosing.
You should display to the user what the current units are. No code is provided for this step.
Practice
- The code above uses polling. Try using events instead to ensure every button press is recorded. For more information, visit the Advanced Lesson: Button Events